What exactly is an electrical isolator?
A device used in electrical systems to physically remove or isolate a circuit from its power supply is known as an electrical isolator. A disconnect switch or a circuit breaker are other names for it. It allows the safe de-energisation and isolation of an electrical circuit section for maintenance, repairs, or emergencies.
The power source in the circuit must be entirely removed for an electrical isolator to properly prevent the flow of electrical current. This isolation is necessary to ensure the safety of anybody working on the circuit or to prevent equipment damage during maintenance or repairs.
Where do Electrical Isolators come in handy?
Electrical isolators are commonly found in industrial infrastructure, electrical panels and switchboards, renewable energy systems, power distribution networks, and other applications.
It’s vital to remember that the specific application and requirements for electrical isolators vary depending on the sector, voltage range, and legal framework of each country. In some instances, electrical engineers or professionals with the requisite expertise must select, install, and use electrical isolators
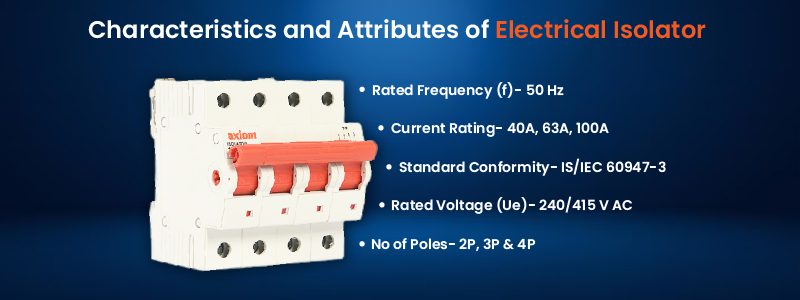
Characteristics and Attributes of Electrical Isolator
SALIENT FEATURES
The Electrical Isolator maximises energy efficiency while requiring minimal electricity and being inexpensive. The Isolators are made to last and are dependable owing to their lengthy electrical and mechanical lifetimes.
The simplicity of energy-efficient, low-watt loss isolators provides a continuous and uninterrupted power supply. Axiom Isolators are meticulously engineered to provide heavy-duty protection while maintaining a small frame size, making them a great choice for a variety of applications. You may have peace of mind knowing that you have invested in the finest with our premium solutions.
TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS
- Standard Conformity:- IS/IEC 60947-3
- No of Poles:- 2P, 3P & 4P
- Current Rating:- 40A, 63A, 100A
- Rated Voltage (Ue):- 240/ 415 V AC
- Rated Frequency (f ):- 50 Hz
Electrical Isolator Common Issues and Maintenance Solution
Electrical Isolators, like any other electrical component, can develop issues that impair their functioning. Here are some frequent electrical isolator difficulties and troubleshooting strategies to fix them:
Loose or corroded connections can cause poor electrical contact, increased resistance, overheating, or even failure. Check that all connections are properly attached and free of corrosion. Check and clean the terminals on a regular basis.
Mechanical Wear: The mechanical parts of isolators can wear out over time, causing difficulty in operation or incorrect switching. Lubricate moving parts as directed by the manufacturer, and replace worn-out components as soon as possible.
Excessive arcing or tracking between switch contacts can cause damage to the isolator and degrade its functionality. Check for evidence of burning, pitting, or carbon deposits in the connections. Maintain good contact alignment by cleaning or replacing broken contacts.
Overheating might occur as a result of continuously high electrical loads or insufficient airflow around the isolator. Ascertain that the isolator is sufficiently rated for the load it will bear and that it is situated in a well-ventilated location. Examine the area for any blockages or dust collection that may be impeding airflow.
Insulation Failure: When insulation fails, it can cause short circuits or leakage currents. Inspect the insulation of the isolator on a regular basis for evidence of deterioration, fractures, or degradation. Replace any damaged insulation as soon as possible.
Incorrect Operation: Incorrect operation, such as using the incorrect switching sequence or exceeding the rated switching frequency, might harm the isolator. Ensure that operators are fully taught proper operation methods and that they follow the manufacturer’s standards.
Assume you have recurrent problems with an electrical isolator that cannot be handled with standard troubleshooting. In that scenario, it is best to seek the advice of a skilled electrician or contact the manufacturer. Always take safety precautions, and only authorised employees should operate on isolators.