Electrical isolators are essential components in electrical systems designed to disconnect circuits from the power supply safely. Their primary role is to ensure that no current flows to specific parts of an electrical circuit during maintenance or fault conditions. This blog will explore electrical isolators’ working mechanisms, benefits, and applications across various industries.
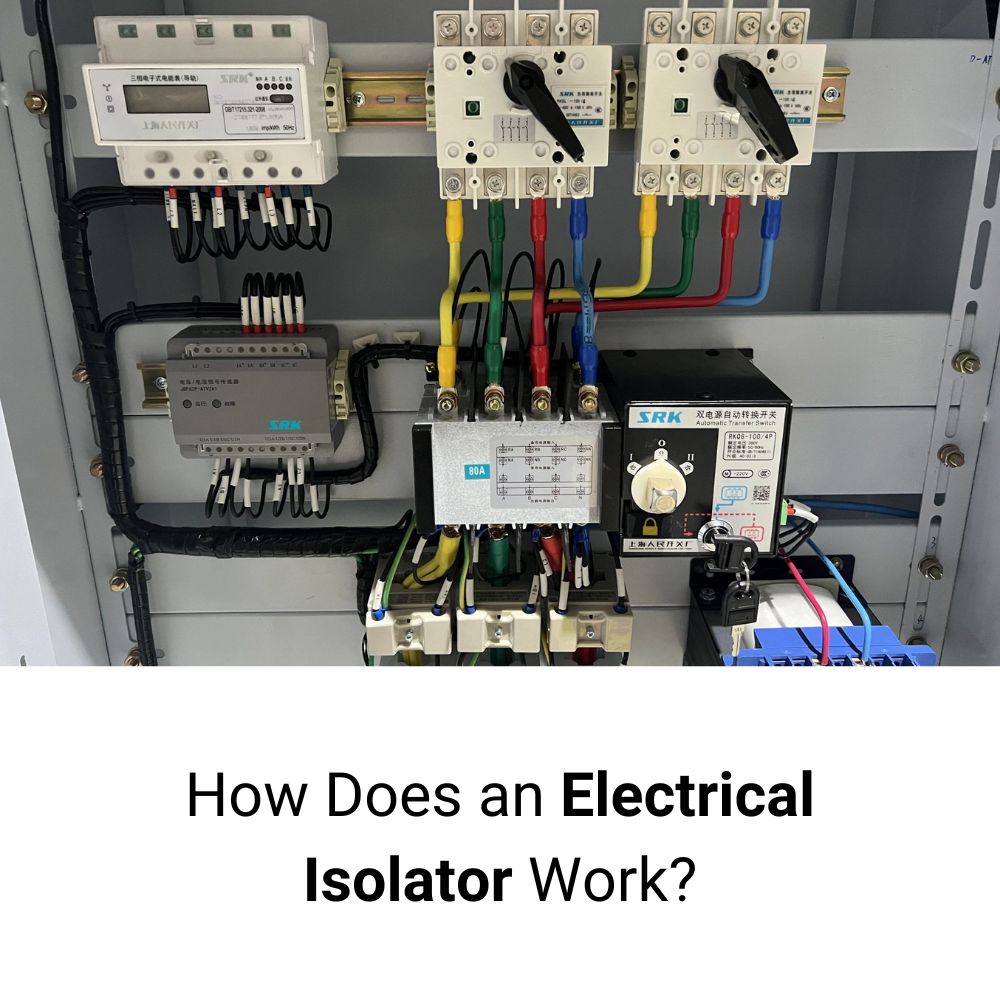
How Does an Electrical Isolator Work?
The fundamental purpose of an isolator switch is to isolate a section of a circuit from the live power supply, which is crucial during maintenance or repair. When an isolator is activated, it opens the circuit, effectively disconnecting the flow of electricity to the equipment or part of the circuit being worked on.
The working mechanism of an isolator involves breaking the circuit at a point where no current is flowing, ensuring that maintenance workers or technicians can safely work without the risk of electric shock. Typically, isolators use physical contacts that open when the switch is turned, cutting off the power supply. This operation is critical in preventing electrical hazards such as fires, short circuits, or damage to equipment.
For instance, a 25A isolator is used in residential or light commercial applications to ensure that all connected electrical devices are completely disconnected from the power source, reducing the risk of electrical accidents. Simply turning the isolator switch de-energizes the system, allowing for safe maintenance.

Key Benefits of Using Electrical Isolators
Integrating isolators into electrical systems offers a wide range of benefits, enhancing the system’s overall safety, efficiency, and reliability.
- Safety: The most significant benefit of isolators is safety. They prevent electrical hazards by completely isolating circuits before work is carried out. Isolators are a vital safety measure that protects workers from the risk of electrical shocks or arc flashes. They are especially critical in industrial and commercial environments with a higher risk of electrical accidents.
- Energy Efficiency: Another essential advantage of isolators is their role in improving energy efficiency. By disconnecting circuits or specific electrical devices, isolators prevent unnecessary power consumption. In large buildings or facilities with multiple operating systems, isolators ensure that power is only used where needed, reducing energy waste.
- Durability and Longevity: High-quality isolators, such as the isolator 25A, are built to last and provide long-term reliability. Constructed from durable materials, these devices can withstand years of use without significant wear and tear. Their reliable performance ensures that they will continue to function effectively, even under demanding conditions, minimizing the need for frequent replacements.
- Prevention of Electrical Hazards: Isolators also play a critical role in preventing potential electrical fires, short circuits, and other hazards. When a system is isolated correctly, the risk of electrical faults that could lead to severe damage is significantly reduced. Whether it’s a 3 phase isolator switch in a commercial setup or an isolator circuit breaker in an industrial application, isolators are designed to keep electrical systems safe from risks associated with power surges or equipment malfunctions.

Applications of Electrical Isolators in Different Industries
Electrical isolators are used across various sectors to ensure the safe operation of electrical systems, from residential homes to large-scale industrial plants. Let’s take a look at how isolators are applied in different industries:
- Residential Use: In residential settings, isolators are often used to disconnect power from specific circuits or appliances for maintenance. The isolator switch allows homeowners or electricians to safely perform repairs or upgrades on electrical systems, ensuring that no current flows through the circuit during work. This is especially useful when dealing with light fixtures, appliances, or other household electrical devices.
- Commercial Applications: Commercial buildings, such as offices or retail stores, rely on isolators to manage power distribution and protect equipment from electrical faults. A 3 phase isolator switch is often used in these settings to isolate high-power systems like HVAC units, lighting circuits, or large machinery. Using isolators, businesses can perform regular maintenance or respond to faults without interrupting the entire building’s electrical system.
- Industrial and Power Plant Applications: In industrial environments and power plants, isolators are vital for disconnecting high-voltage equipment, such as transformers, circuit breakers, and generators. These settings require isolators to handle much larger currents, and their role in preventing electrical hazards is critical. Whether using an isolator circuit breaker or a vacuum isolator, these devices ensure that equipment remains protected from damage while maintenance work is carried out safely.
- Utility and Substation Systems: Electrical substations, where high-voltage equipment is located, rely heavily on isolators to manage and maintain power transmission networks. In substations, isolators are used to de-energize sections of the electrical grid, allowing technicians to conduct maintenance safely. The isolator circuit breaker is frequently used in these environments to isolate sections of the grid during fault conditions, preventing potential damage to sensitive equipment and ensuring a stable power supply.

Conclusion: The Vital Role of Electrical Isolators in Ensuring Safety and Efficiency
Electrical isolators are indispensable in ensuring electrical systems’ safe and efficient operation. Whether it’s a 25A isolator in a residential setup or a 3-phase isolator switch in a commercial or industrial setting, these devices provide essential protection and contribute to the overall longevity of electrical systems. With their ability to isolate circuits, prevent electrical hazards, and enhance energy efficiency, isolators are critical in modern electrical infrastructure.